
Asphodelus tenuifolius /كوثر
Asphodelus fistulosus L.var tenuifolius(Cav.)Baker
Boroq, Barwaq, Kawthar, Shrbas, Bosail,Basal Iblees,Basal AlShaitan, Dhmaikh
Asphodel; Hollow-stemmed asphodel
Kufer, Kawther, Kowaitah
Liliaceae

Flowers

Plant habitat
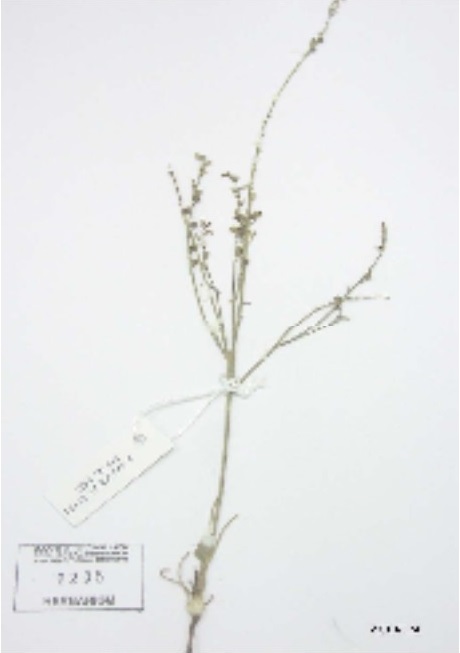

Herbarium Sample
Ethnobotanical Characteristics
Description
Erect, glabrous annual herb with a perennial bulb, erect hollow cylindrical stem up to 50 cm high, shorter than scape. Leaves linear, simple, semiterate, fistulose tapering, ½ as long as the scapes, 1-2 cm wide. Inflorescence panicle, bracts triangular, acuminate, whitish-scarious with a keeled nerve; flowers small, perianth c. 3mm long, campanulate; whitish pink with maroon veins in center of each petal. Fruit capsule , obovoid, 3-valved and light brown. Seeds few, triangular, pitted, black grayish in color, c. 2-3 mm long, finely and shortly papillose.
Habitat & Distribution
Widespread in many regions, warm or temperate of the world. In U.A.E the plant is common in dry slopes and damp areas of the mountains in the northern emirates and Al-Ain, and in cultivated fields, it flowers in spring.
Part(s) Used
Bulb and seeds
Traditional & Medicinal Uses
Whole plant is spasmogenic, stimulant, laxative, diuretic and crushed plant used to treat ulcer; used to make cakes of boiled curdled milk(`iqt`); the seeds good for toothache.
Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry
Parts studied
Aerial pars (stem, leaves).
Microscopical Description
A transverse section of a leaf shows a thick cuticle covering thin-walled significantly elongated epidermal cells somewhat squared at the narrow ends; thus the parenchyma appear to be arranged in a parallel form. The stomata are large, ovoid and are found between the squared ends of the adjacent epidermal cells. The palisade cells have different sizes and seem to be in two layers but they are loosely arranged. The spongy mesophyll cells are mostly round but also they vary in size and are loosely arranged. The mesophyll embed vascular strands including spirally and annularly thickened vessels, elongated associated parenchyma cells and fibers. They also embed scattered round to ellipsoid idioblasts containing acicular crystals of calcium oxalate that occur in bundles and together with elongated structures that seem to be ducts tapering at both ends and filled with yellow to orange contents. Stem epidermal cells are largeelongated parenchyma. The inner parts of the stem include elongated parenchyma, compactly arranged fibro-vascular strands including pitted tracheids, large annularly, spirally or reticulately thickened vessels. Some of the stem large parenchyma cells are almost filled with orange-brown coloured contents.
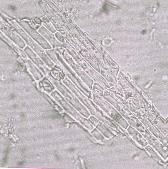
a) Epidermal cells

b) Thickened vessels
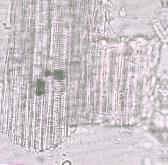
c) Fibro-vascular strands
- (a) Surface view of a leaf fragment showing the significantly elongated epidermal cells arranged in a parallel manner with the oval stomata existing between the squared terminal ends of the adjacent cells.
- (b) A fragment of leaf vascular tissues showing adjacent annularly and spirally thickened vessels with their accompanying short fibers.
- (c) A fragment of the stem showing the compactly arranged fibro-vascular strands including pitted tracheids and large vessels which are either annularly, spirally or reticulately thickened (Magnifications: x 250, x 400 and x 250, respectively).
Organoleptic characteristics
Appearance: Solid powder
Colour: Light brown
Odour: Odorless
Taste: Slightly bitter
Physicochemical constants
Loss in weight on drying at 105 °C (%): 5.20-6.40
Solubility
Alcohol solubility (%): 4.80
Water solubility (%): 24.80-26.40
10% ethanolic extractive (%): 31.86
Ash values (%)
Total ash: 8.40-9.00
Water soluble ash: 20-2.40
Acid-insoluble ash: 0.20
Successive extractive (%)
Petroleum ether (60-80 °C): 02.0
Chloroform: 2.00
Absolute alcohol: 6.40
Distilled water: Not done
pH values
pH of 1% solution: 5.32-5.43
pH of 10% solution: 4.99-5.12
Chemical constituents
Leaves and seeds contain anthraquinones (aloe-emodin, chrysophanol), sterols, and terpenoids, flavonoids, sugars, fatty acids and oils (DPS, ZCHRTM unpublished results, Shahina 1994).
Pharmacological and Toxicological studies
1. Ethanolic Extract 10%
The plant extract showed significant stomach protection against this model of ulcerogenesis (Gurbuz et. al., 2002). The plant showed antifungal activity, the Trichophyton violaceum was the most susceptible being completely inhibited by 50% of the extract. (Ali and Abu, 1999a; Ali and Abu, 1999b).
The pharmacological and toxicological studies carried out in our laboratory and the results in brief, on Aspholdelus tenuifolius (10% ethanolic extract) have been given below.
The results presented without references showed unpublished data (unpublished results, ZCHRTM, DBMS):
|
ACTIVITY |
RESULTS |
|
Anti-inflammatory activity-Rat paw oedema |
Extract showed significant anti-inflammatory activity. |
|
Antinociceptive activity-Writhing |
Extract showed significant antinociceptive activity in one model only. |
|
Effect on GIT smooth Muscle-Isolated rabbit intestine |
Reduced amplitude of contraction. |
|
Effect on GIT smooth Muscle-Isolated rat fundus |
Produced slight contraction. |
|
Acute toxicity studies |
Produced no toxic symptoms. |
|
LD50 evaluation |
>10 g/kg. |
Summary of the results (10% ethanolic extract)
Aspholdelus tenuifolius (10% ethanolic extract) has been found as good antiinflammatory and antinociceptive agent.
2. Aqueous Extract
The pharmacological and toxicological studies carried out in our laboratory and the results in brief, on Aspholdelus tenuifolius (Aqueous extract) have been given below.
The results presented without references showed unpublished data (unpublished results, ZCHRTM, DBMS):
|
ACTIVITY |
RESULTS |
|
Anti-inflammatory activity-Rat paw oedema |
No significant anti-inflammatory activity observed. |
|
Effect on GIT smooth Muscle-Isolated rabbit jejunum |
Produced long lasting reduction in the contraction. |
|
Effect on GIT smooth Muscle-Isolated rat fundus |
Produced contraction. |
|
Gross behavioral studies-Tremor/Twitches |
No tremors observed. |
|
Gross behavioral studies-Writhing |
No writhing observed. |
|
Gross behavioral studies-Diarrhea, Urination |
No diarrhea and urination. |
|
Mortality |
No mortality recorded. |
|
Motor co-ordination (String &Platform test) |
Motor coordination not affected. |
|
Acute toxicity studies |
Not toxic symptoms observed. |
|
LD50 evaluation |
>10 g/kg. |
Summary of the results
Aspholdelus tenuifolius (aqueous extract) showed strong anti-inflammatory activity. Acute toxicity study showed that this plant appears safe. However, chronic toxicity study is required before its human use.
Antimicrobial activity
The plant showed antifungal activity, the Trichophyton violaceum was the most susceptible being completely inhibited by 50% of the extract( Ali& Abu -Ghdeib 1999).
References
- Ali-Shtayeh MS, Abu Ghdeib SI. Antifungal activity of plant extracts against dermatophytes. Mycoses. 1999; 42(11-12): 665-72.
- Department of Biomedical Sciences, Zyed Complex for Herbal Research and Traditional Medicine, Unpublished results.
- Department of Pharmacognostic Sciences, Zyed Complex for Herbal Research and Traditional Medicine (ZCHRTM), unpublished results.
- El-Ghonemy, A. A. Encyclopedia of Medicinal Plants of the United Emirates. (1993) 1st Edition, University of U.A.E.
- Ghazanfar S A ., Handbook of Arabian Medicinal Plants., CRC Press, p.131, 1994 .
- Gurbuz I, Ustun O, Yesilada E, Sezik E, Akyurek N. In vivo gastroprotective effects of five Turkish folk remedies against ethanol-induce dlesions. J Ethnopharmacol. 2002 Dec; 83(3): 241-4.
- Kotb, T. F. Medicinal Plants in Libya.(1985) Arab Encyclopedia House; Tripoli-Libya.
- Liu, XM., Zakaria MN., Islam, MW., Radhakrishanan, R., Ismail, R.., Chen, HB., chan, K., Al-Attas, (2000) A. anti-inflammatory andantiulcer activity of C. Comosum in rats. Fitoterepia 72(5); 487-91.
- Mandaville, J.P. Flora of Eastern Saudi Arabia. (1990) Kegan Paul International Ltd. England.
- Western, A. R. The Flora of United Arab Emirates, an introduction. (1986) Publication of the U.A.E University.
- كریم، فوزي .الأعشاب في دولة الإمارات العربیة المتحدة، ( 1995 ) مطبعة جامعة الإمارات
