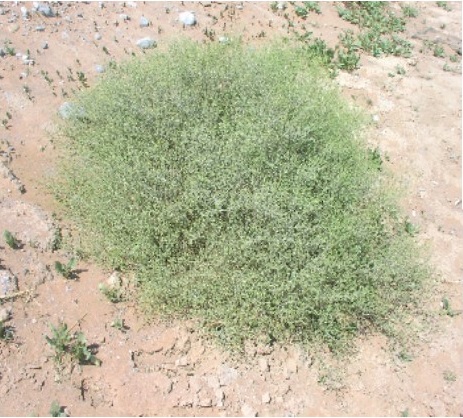

Fagonia indica / الشكاع
F. parviflora Boiss
Shokaa, Shokai, Showika, Aataf, Aaqol, Shokah Baidaa, Janab Shokai
Fagonia
Shoka`a
Zygophyllaceae
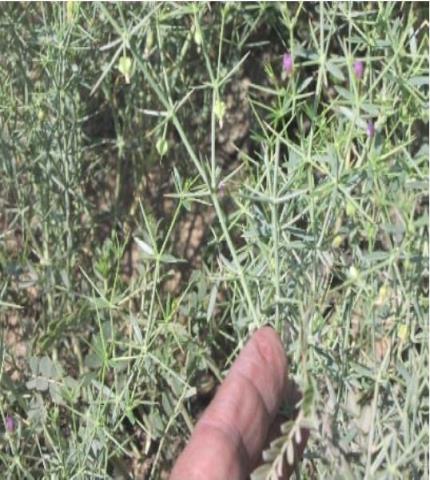

Flowers

Herbarium Sample
Ethnobotanical Characteristics
Description
Perennial, minutely and densely glandular, very much branched desert herb up to 80 cm. Stem with woody base, finely striate but terete; only the highest internodes sulcate. Leaves unifoliate, elliptical to linear- lanceolate, acute, mucronate, 8-15 mm long; petioles variable, 1-3 mm long. Stipular spines on swollen nodes, 5-20 mm long, shorter or exceeding the leaves. Flowers solitary in the axils, fragrant, to 12mm in diameter, pedicels 3-8 mm long, with pink to purple petals. Fruit a capsule 3-5 mm long, 2-5 mm wide, short pubescent with persistent style. Seeds flat rounded and brown in color.
Habitat & Distribution
Found in deserts and dry areas from India to Tropical Africa and in Chile as well as USA. In UAE it is widespread, found in shallow sands over gravels or limestone, hillsides and wadis.
Part(s) used
whole plant
Traditional & Medicinal Uses
In UAE, decoction of dried leaves or fresh juice of whole plant are used for stomach problems, fever and skin problems (itching, wounds). In other countries the plant is used for high acidity, gonorrhea, skin problems; stomachic, tonic, expectorant, anti-inflammatory, vulnerary, good for hepatic problems, fever, swellings, wounds and kidney stones.
Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry
Parts studied
Leaves and branches
Microscopic Description
Leaf :In a surface view, both epidermises consist of polygonal cells with slightly thickened straight cell walls. A transverse section of the leaf shows its isobilateral character. Both epidermises consist of small rectangular cells with slightly thickened straight cell walls covered with a thick striated cuticle. The palisade tissues consist of two layers of compactly packed cells with thin straight walls. The spongy tissues almost consist of small spherical cells and are traversed by vascular tissues that contain angular annularly thickened vessels. Both palisade and spongy tissues are rich in light green needles and rosettes or crystalline materials. Stomata are oval and anomocytic in type and they are fairly distributed on both epidermises.
Branch: A transverse section of the branch is cordate to kidney-shaped in outline. The epidermis consists of small rectangular uniform cells with thick cells walls covered by a thick cuticle. The outer layer of the cortex consists of round to polygonal cells followed by several layers of oblong cells. Scattered in the cortex are many vascular bundles with annularly thickened vessels and many short compactly packed fibers with markedly thick walls. The pith consists of hexagonal cells with different sizes and slightly thick cell walls; those existing at the center are larger. Crystalline and amorphous substances are frequent in the cortex and pith (DPS, ZCHRTM unpublished results).
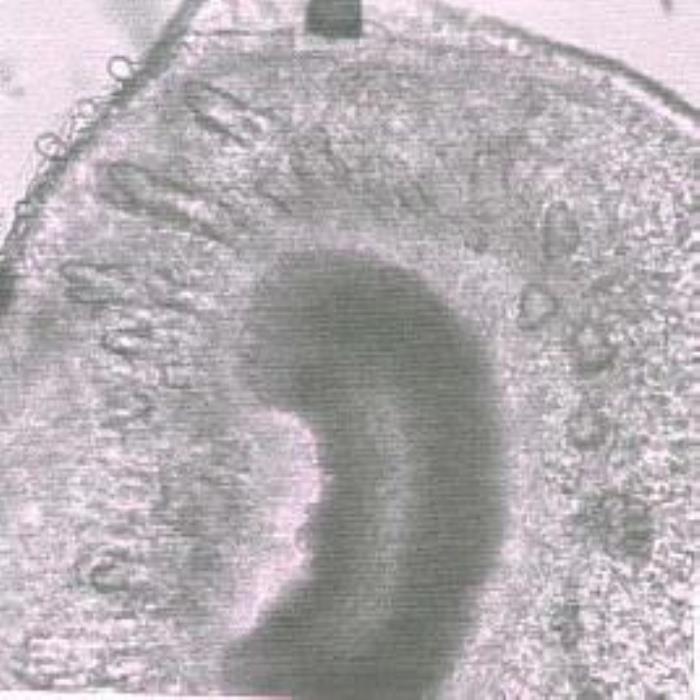
a) TS of branch
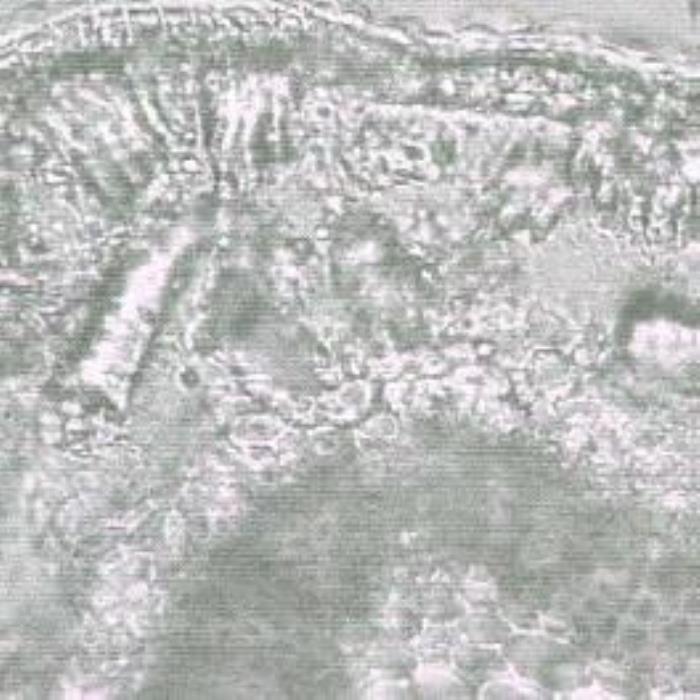
b) Detailed TS of branch
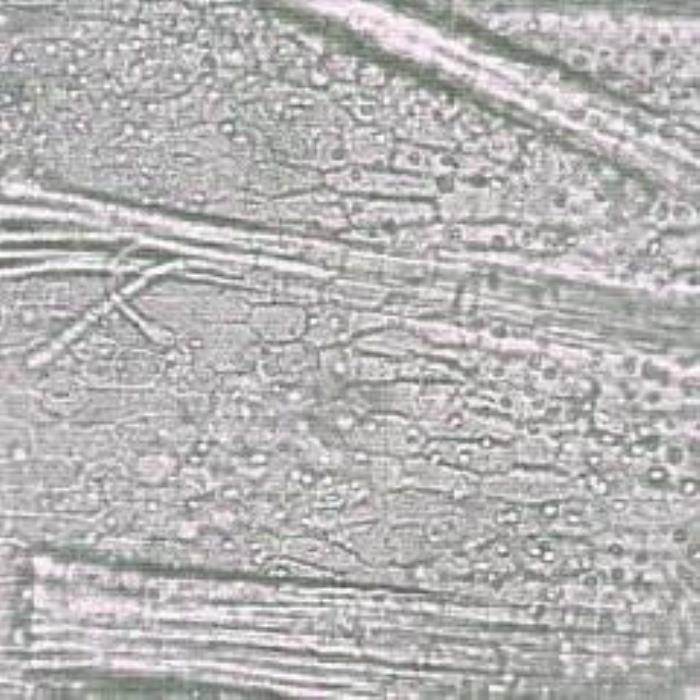
c) Surface view of leaf
- (a). TS of a branch showing the epidermis with thick cuticle followed by cortex parenchyma (embedding zones of bundles of fibers), the endodermis, then crescent shaped vascular tissues (dark-coloured) and pith (less dark).
- (b). Detailed TS of a branch showing the outer small rectangular epidermal cells followed by oblong cortical parenchyma cells, a zone enclosing bundles of fibers, inner layers of cortex, endodermis, a circle of vascular tissues (dark) and hexagonal pith cells. The epidermis is covered with a thick cuticle.
- (c). Surface view of the inner part of the leaf epidermis polygonal cells showing the granular contents of the cells, stomata and groups of fiber bundles encircled by cortical parenchyma cells. ( Magnifications: All x 250).
Organoleptic characteristics
Appearance: Fine powder
Colour: Light green
Odour : Aromatic
Taste : Bitter
Physicochemical constants
Loss of weight drying at 105 °C(%): 8.20-8.80
Solubilities(%)
Alcohol solubility: 02.40
Water solubility: 17.60
10% alcoholic extractives : 27.56
Ash values (%)
Total ash: 8.40-8.60
Water soluble ash: 2.80
Acid insoluble ash: Nil
Successive extractives (%)
Petroleum ether (60-80°C): 1.00
Chloroform: 0.90-1.00
Absolute alcohol: 4.70-5.00
Distilled water: 18.80-19.50
pH values
pH of 1% aqueous solution: 6.02
pH of 10% aqueous solution: 5.72
The above results are under process of publication (DPS ZCHRTM un pub results).
Chemical constituents
Triterpenoid, saponins, alkaloids, coumarins, flavonoids and tannins. (DPS, ZCHRTM un pub. results; Ghazanfar 1994).
Pharmacological and Toxicological studies
Effects of powdered Fagonia cretica plant and triterpenoid from its ethanolic extract showed that the saponins had highly significant decreasing effects on the amount of total leukocyte count of rabbit's blood (Asif et. al., 2003). The plant leaf extracts were found most effective against Salmonella typhi. (Geholt et. al., 2000). The plant extract showed mollusuicidal activity(Shoeb et. al., 1987). New erythroxane-type diterpenoids from Fagonia showed cancer-preventing agent (Gedara et. al., 2003).
The pharmacological and toxicological studies carried out in our laboratory and the results in brief, on Fagonia cretica (10% ethanolic extract) have been given below. The results presented without references showed unpublished data (UPD, ZCHRTM, DBMS):
|
ACTIVITY |
RESULTS |
|
Anti-inflammatory activity-Rat paw oedema |
Significant anti-inflammatory activity(Liu et al., 2001). |
|
Anti-inflammatory activity-Cotton pellet |
Significant anti-inflammatory activity (Liu et al., 2001). |
|
Antinociceptive activity-Writhing |
Showed no analgesic activity (Liu et al.,2001). |
|
Anti-hypertensive activity-Anesthetic rats |
No effect on BP & HR observed. |
|
Vasorelaxant activity-Isolated aortic strip |
No relaxation produced in Na contracted strip. |
|
Cardiotonic activity & HR Isolated rat atria |
Increase in force of contraction, very significantly reduced the rate observed. |
|
Effect on GIT smooth Muscle-Isolated guinea pig ileum |
No change in resting tension noted. |
|
Effect on GIT smooth Muscle-Isolated rabbit jejunum |
No effect of amplitude or frequency of contraction reported. |
|
Gross behavioral studies-Tremor/Twitches |
No toxicity observed. |
|
Gross behavioral studies-Writhing |
No toxicity observed. |
|
Gross behavioral studies-Diarrhea, Urination |
No abnormal signs recorded. |
|
Mortality |
No death recorded. |
|
Motor co-ordination (String &Platform test) |
Motor coordination not affected. |
|
Anti-asthmatic activity-Tracheal chain |
No relaxation in histamine- contracted chain reported. |
|
Acute toxicity studies |
No toxicity observed |
|
LD50 evaluation (i.p.) |
987.4 mg/kg. |
Summary of the results
Fagonia (10% ethanolic extract) showed significant anti-inflammatory activity. Fagonia extract also showed no signs of toxicity on acute administration.
Antimicrobial activity
The plant leaf extract was found most effective against Salmonella typhi (Geholt & Bohra 2000).
References
- Asif Saeed M, Wahid Sabir A., (2003) Effects of Fagonia cretica L. constituents on various haematological parameters in rabbits. J Ethnopharmacol. 85(2-3): 195-200.
- Department of Biomedical Sciences, Zayed Complex for Herbal Research and Traditional Medicine, Unpublished results.
- Department of Pharmacognostic Sciences, Zayed Complex for Herbal Research and Traditional Medicine ( ZCHRTM ), unpublished results.
- El-Ghonemy, A. A. Encyclopedia of Medicinal Plants of the United Emirates. (1993) 1st Edition, University of UAE.
- Gedara SR, Abdel-Halim OB, el-Sharkawy SH, Salama OM, Shier TW, Halim AF. , (20030 New erythroxane-type diterpenoids from Fagonia boveana (Hadidi) Hadidi & Graf. Z Naturforsch 58(1-2): 23-32.
- Gehlot D, Bohra A., Antibacterial effect of some leaf extracts on Salmonella typhi. Indian J Med Sci. 2000 Mar; 54(3): 102-5.
- Ghazanfar S A. Handbook of Arabian Medicinal Plants CRC Press, p.216, 1994
- Ghazanfar, S.A. Handbook of Arabian Medicinal Plants (1994) CRC, Library of Congress.
- Jongbloed, M.V. The Comprehensive Guide to the Wild Flowers of the united Arab Emirates, Erwda, (2003) Emirates Printing Press, Dubai, U.A.E.
- Kotb, T. F. Medicinal Plants in Libya. (1985) Arab Encyclopedia House. Tripoli-Libya.
- Liu, X.M., Islam, M.W., Radhakrishnan, R, , Ismail, Chen, H.B. A, Al- Naji, M.A. Evaluation of anti-inflammatory activity of Fagonia indica in rats. International Congress and 49th Annual Meeting of the Society for Medicinal Plant Research (Gesellschaft for Arzneipfianzenforschung), September 2-6, 2001, Erlangen, Germany.
- Mandaville, J. P. Flora of Eastern Saudi Arabia. (1990) Kegan Paul International Ltd. England.
- Shoeb HA, El-Emam MA, Saad AM, Mohamed MA. (1987) Molluscicidal activity of Fagonia cretica and Atriplex leucoclada. J Egypt Soc Parasitol. 17(2): 539-46.
- Western, A. R. The Flora of United Arab Emirates, an introduction. (1989) Publication of the UAE University.
